Myanmar: +95(9)445652455 / Japan: 09029359016
What is Myanmar?

ABOUT OF
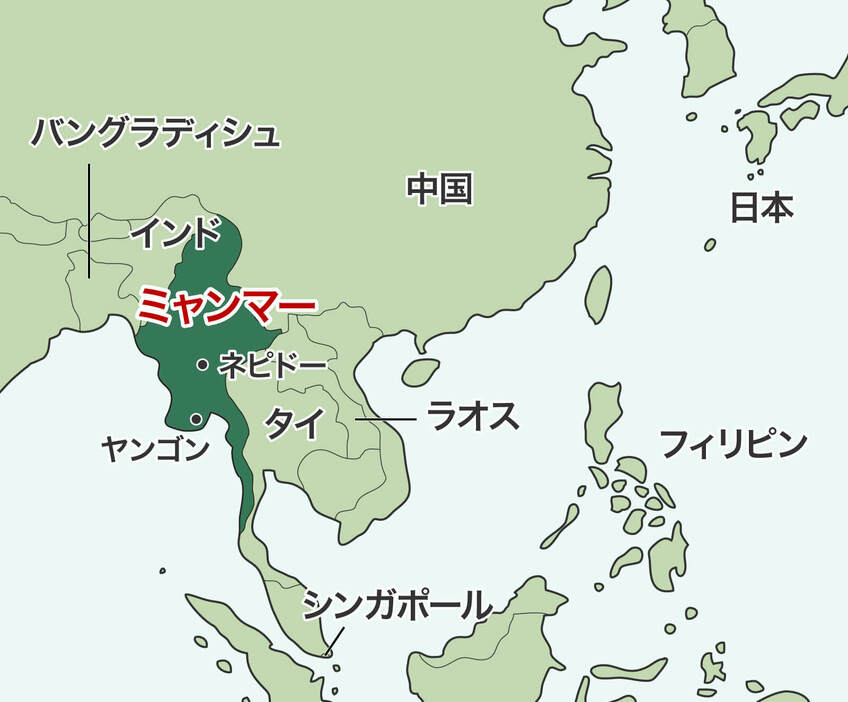
ミャンマー連邦共和国
-
総人口:5,457万人 (2023年9月)
-
国土 :68万平方キロメートル
-
民族 :ビルマ族(約70%、その他多くの少数民族)
-
宗教 :仏教(90%)、キリスト教、回教等
-
一人当たりのGDPは推定1,278ドル(約13.5万円)です。日本は44,246ドル(約470万円)なので日本のおよそ34分の1ということになります。

ミャンマーは同じアジアですが、日本からは遠い所にあります。日本へは約8時間、ミャンマーへは約6時間かかります。 成田国際空港から直行便に乗ることも可能です。



-
00
㎢Area
-
00
Population (2022 estimate)
-
00
billionGross domestic product (2023 estimate)







Myanmar
A brief history of Myanmar
The history of Myanmar (also known as Burma; Burmese: မြန်မာ့သမိုင်း) covers the
period from the time of first-known human settlements 13,000 years ago to the
present day. The earliest inhabitants of recorded history were a
Tibeto-Burman-speaking people who established the Pyu city-states ranged as far
south as Pyay and adopted Theravada Buddhism.
Another group, the Bamar people, entered the upper Irrawaddy valley in the early
9th century. They went on to establish the Pagan Kingdom (1044–1297), the
first-ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. The Burmese
language and culture slowly came to replace Pyu norms during this period. After
the First Mongol invasion of Burma in 1287, several small kingdoms, of which the
Kingdom of Ava, the Hanthawaddy Kingdom, the Kingdom of Mrauk U and the Shan
States were principal powers, came to dominate the landscape, replete with
ever-shifting alliances and constant wars.
Myanmar
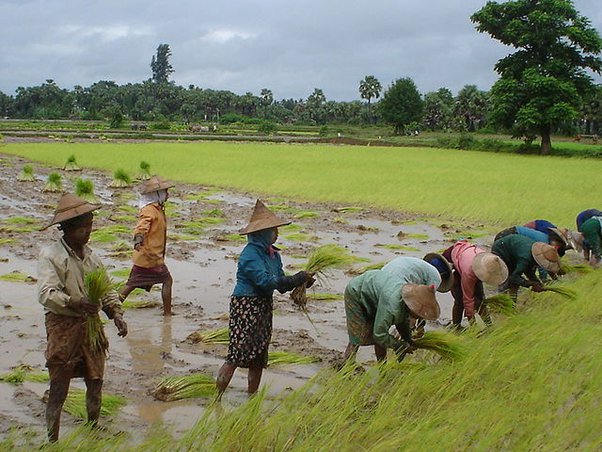
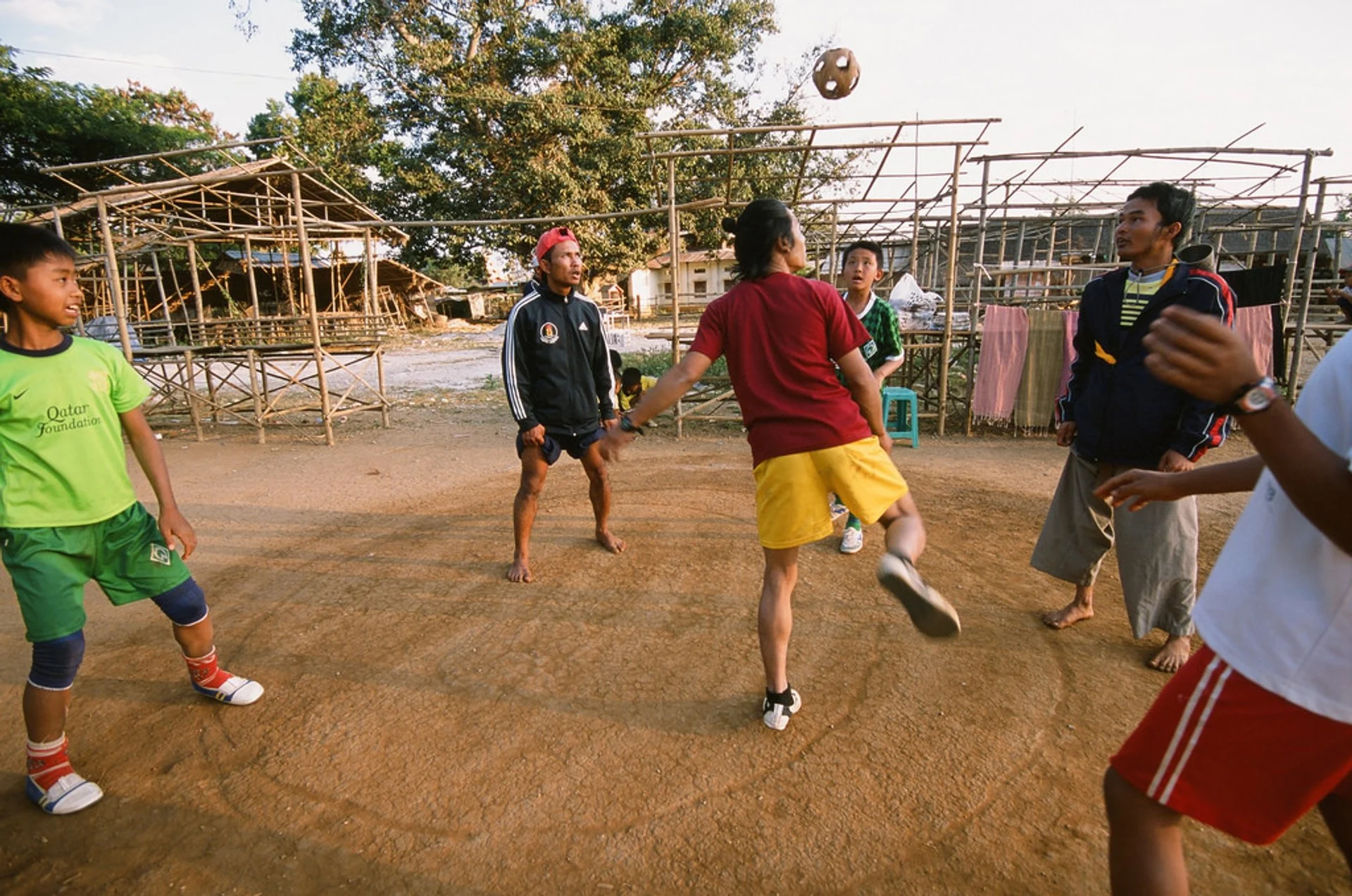
People & Society

The Republic of the Union of Myanmar has a population of over 51 million (2014
Census). The major racial groups are Bamar, Kachin, Kayah, Kayin, Chin, Mon,
Rakhine and Shan. The people are called Myanmar. Over 80 percent of Myanmar
embraces are Theravada Buddhism. There are Christians, Muslims, Hindus and some
animists.
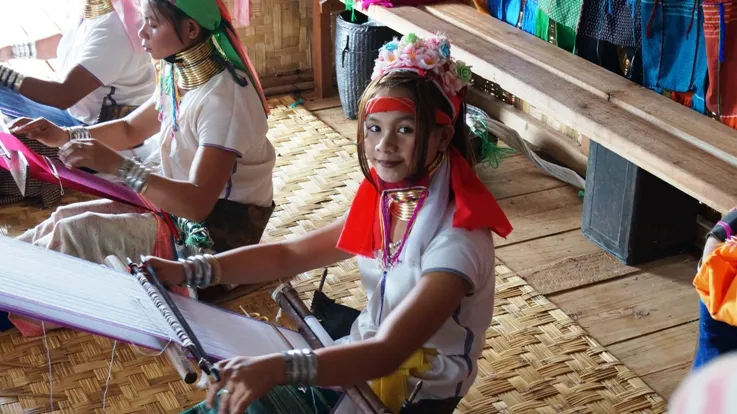
Predominantly Myanmar (Bamar) and ethnic minorities speaking Chin, Kachin,
Kayin, Shan and overall 135 distinguishable ethnic groups dialects and also
Cantonese, Mandarin, Hindustani, Urdu spoken Chinese and Indian Immigrants.
Being once a British colony English is also widely spoken.
Myanmar
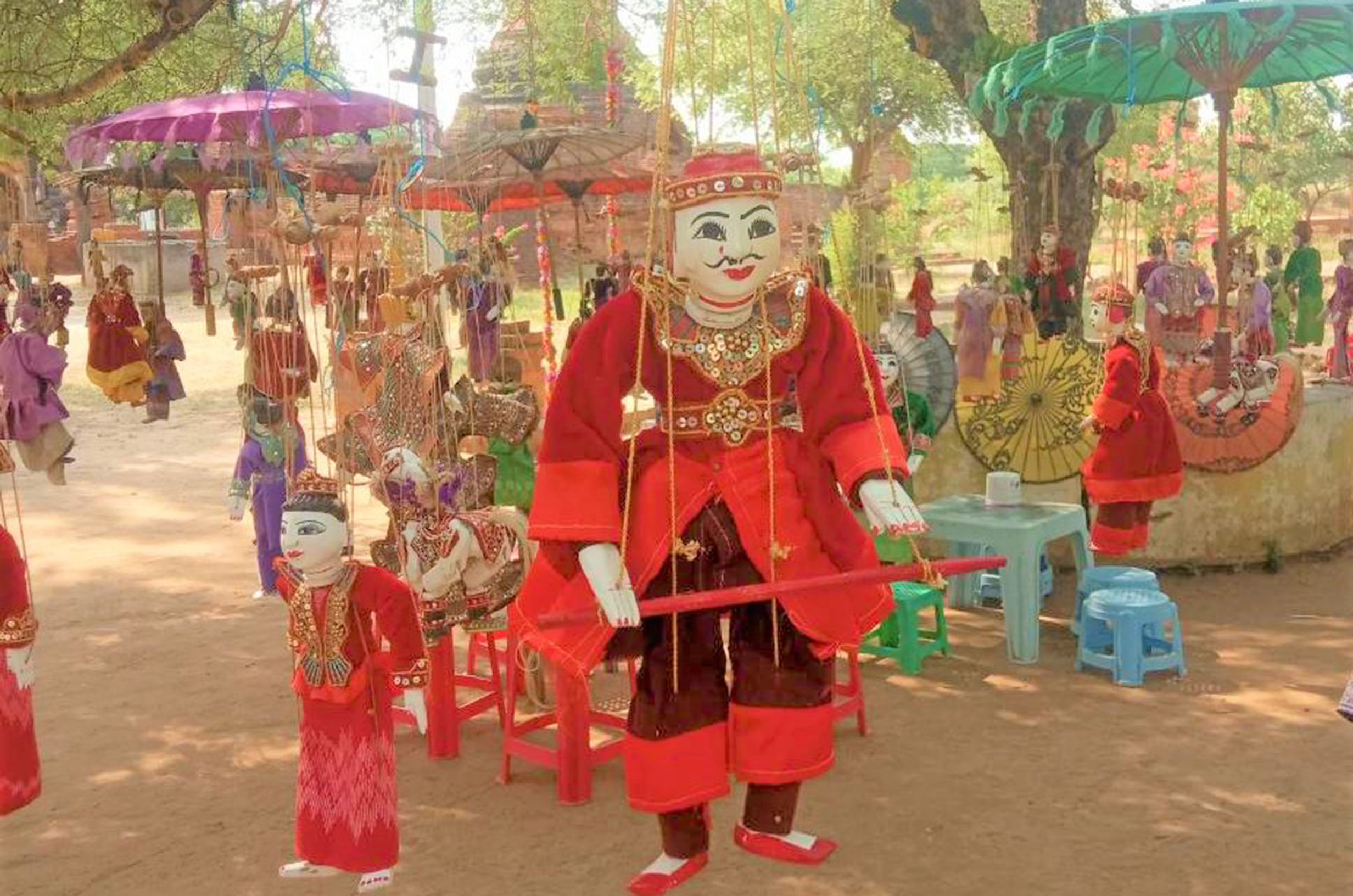
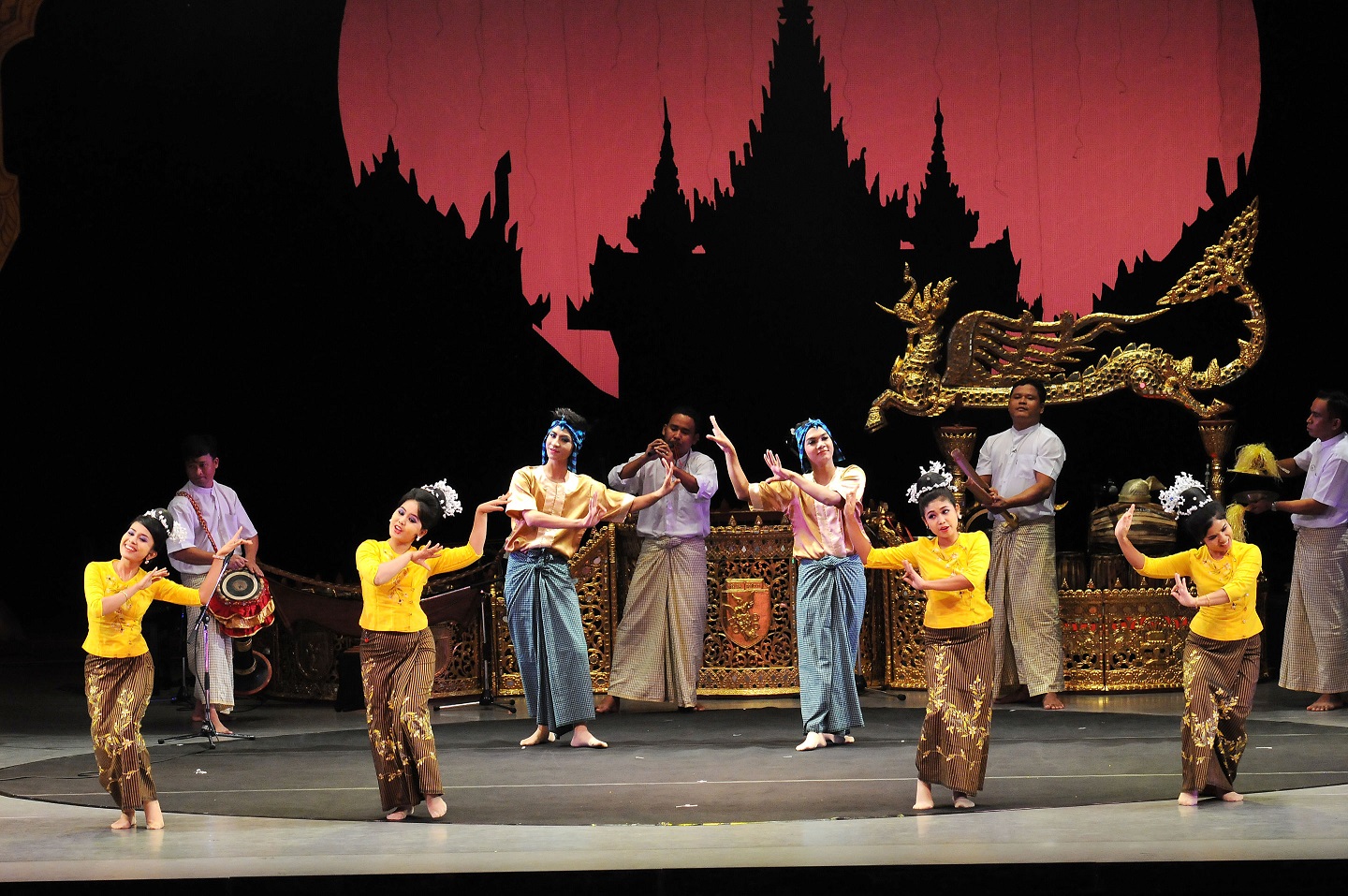
Culture & Heritage

Culture is a part of human life. It comprises our values, beliefs, customs,
languages and traditions those are descended comprises from generation to
generation.
UNESCO defines culture as the set of distinctive spiritual, material,
intellectual and emotional features of society or a social group, that
encompasses, not only art and literature, but lifestyles, ways of living
together, value systems, traditions and beliefs.(UNESCO, 2001).
Cultural heritage can be comprised as tangible culture (such as ancient
buildings, monuments, landscapes, books, works of art, and artifacts),
intangible culture (such as folklore, traditions, language, and knowledge), and
natural heritage (including culturally significant landscapes, and
biodiversity).
...
Upgrading the living standard of human being is also a way of upgrading the
cultural standards. Flourishing the religious doctrine under the guidance of
customs, attitudes, behaviors and compassion flourishing the establishing
the modernized and civilized societies; understanding and appreciating
culture and arts that were flourished over time, and cultivating and
preserving these good traditions are the essence of culture.
As Myanmar is a union inhabited by more than 100 ethnic groups, it has
abundant diverse cultural heritage. According to the one of the social
objectives “Uplifting the national prestige and integrity and preservation
and safeguarding of cultural heritage and national character” laid down by
the State and the Ministry of Religious Affairs and Culture has set a
mission to "protect and develop Myanmar's traditional cultural heritage and
make citizen to love and cherish the Myanmar culture", and efforts are being
made to preserve Myanmar's traditional cultural heritage in line with the
international standards.
Myanmar
Festivals

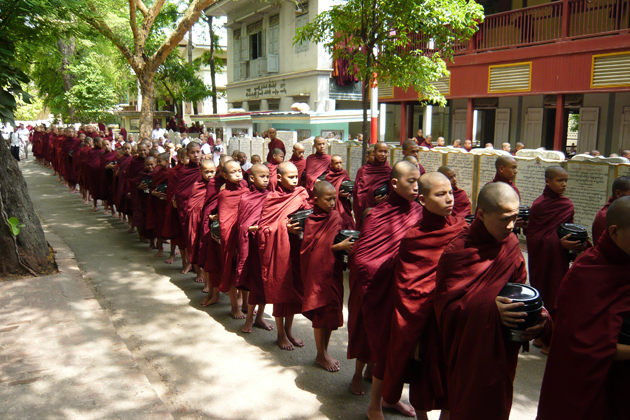
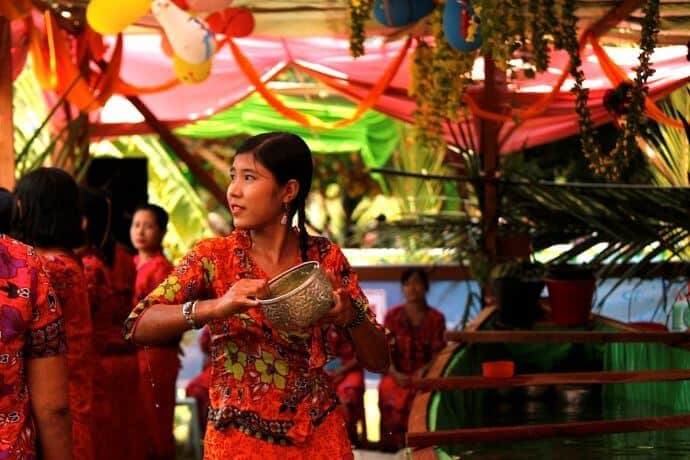
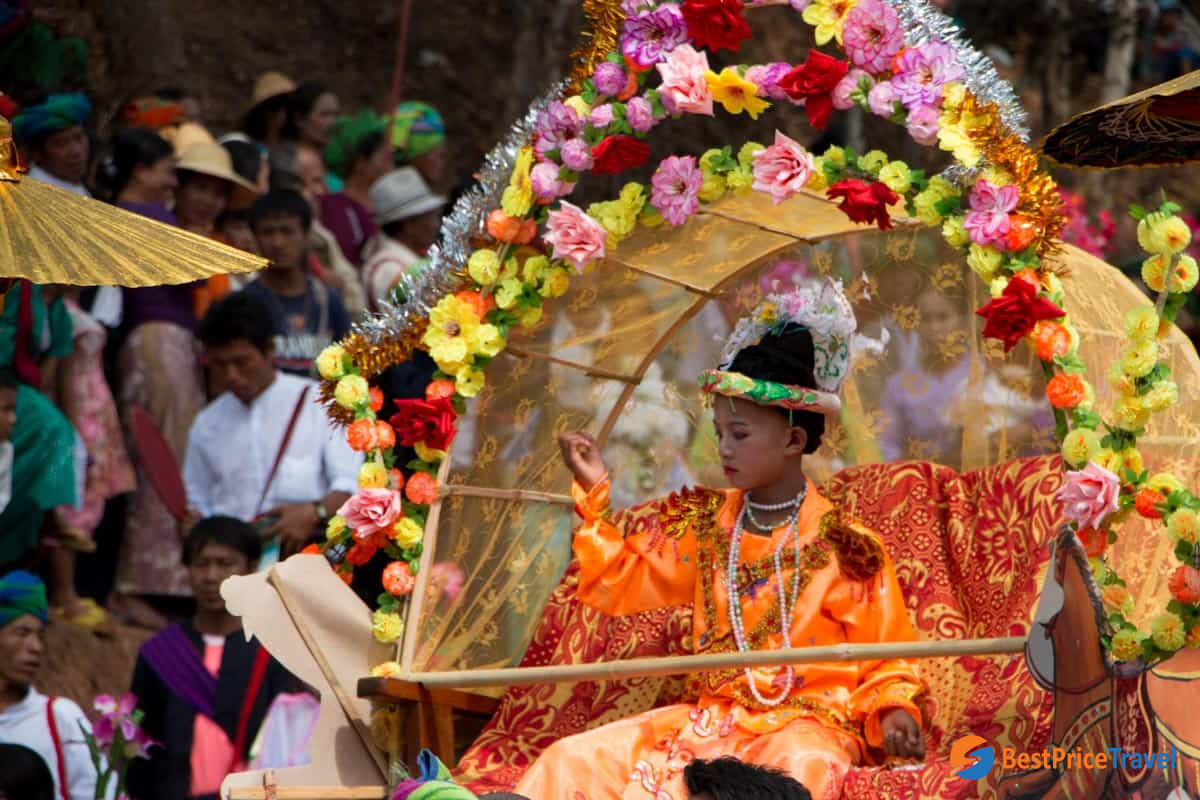
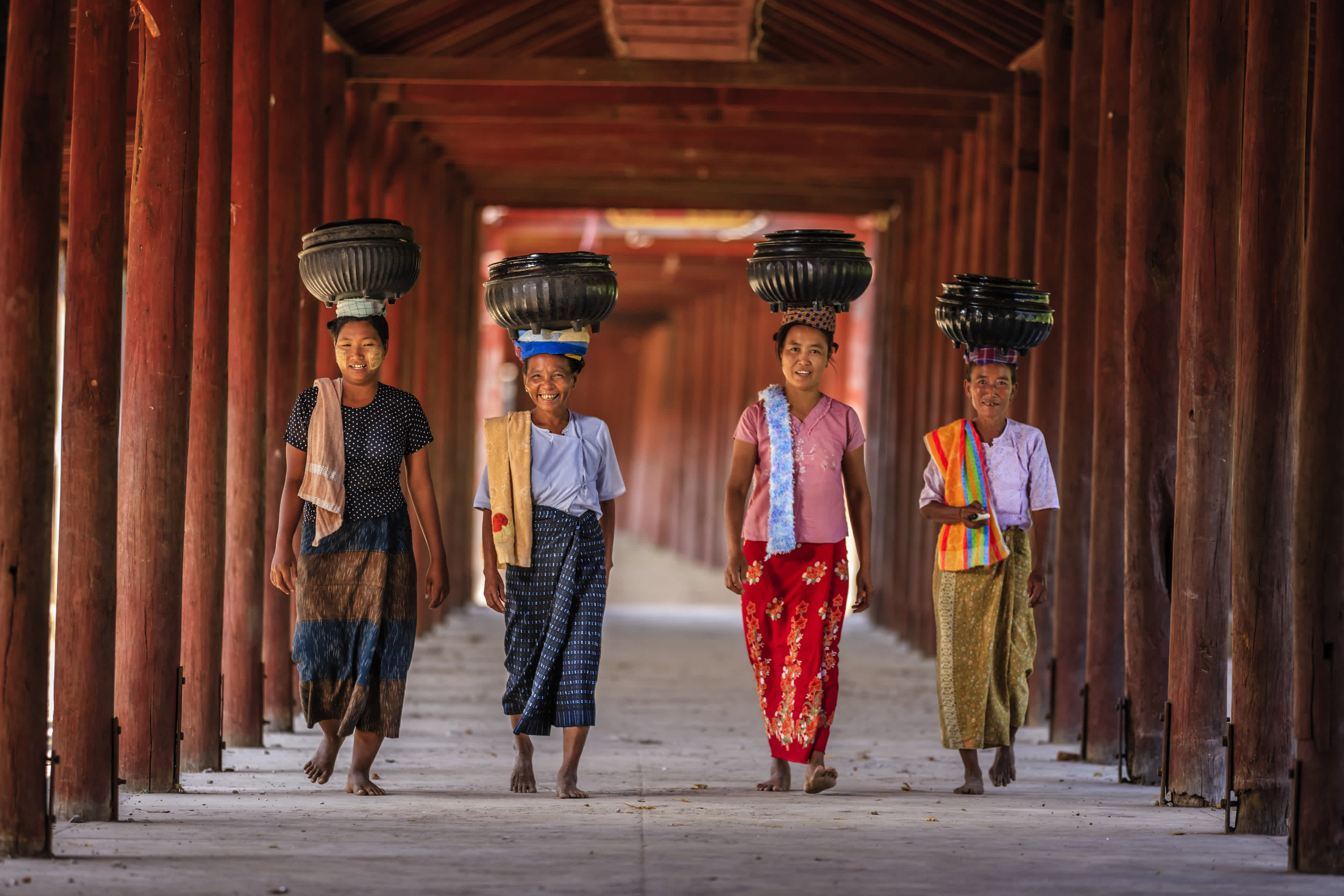
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar is a country with the biggest cultural heritage in Southeast Asia. The Burmese calendar is populated with the "12 seasonal festivals", born from the religious, social, political and educational customs and traditions of the ancient Myanmar people. These festivals are Myanmar's sacred thousand-year-old legacy, preserved throughout the ages. They also have various beneficial effects such as encouraging an influx of academics, propagating Buddhism, and bringing about prosperity for the nation.
Myanmar
Travel Myanmar

Mingalabar is a word of welcome as well as a wish for good fortune. This single
word best signifies the inherent nature of the people of Myanmar: not only to
offer hospitality but to wish others well. With traditions deeply rooted in the
loving-kindness philosophy of Buddhism, the creed the Myanmar lives by is
cedana, or heart-felt goodwill towards friends and strangers alike. Myanmar
possesses a rich and vibrant cultural tradition. Great natural beauty combines
with magnificent temple architecture.
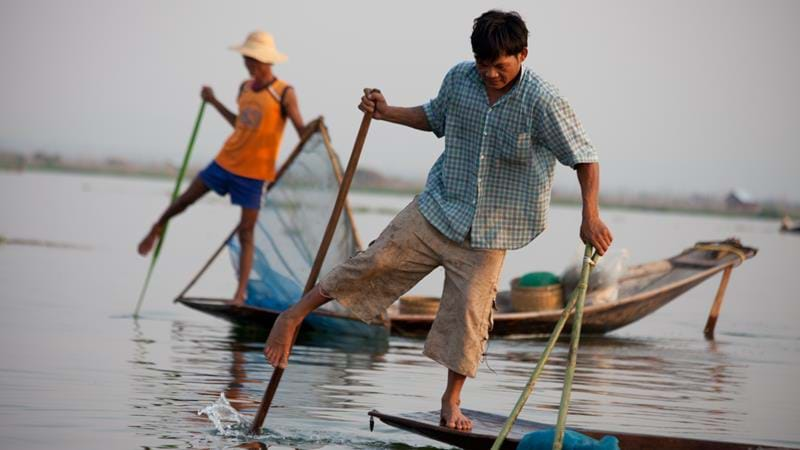
Traditionally, Myanmar tourism is based on culture. Myanmar with its long
history, culture and religion has many pagodas, temples and monuments all over
the country. In addition, Myanmar is also blessed by nature with natural
attractions. There are snow-capped mountains, deep forests, cool and scenic
places, long rivers, beautiful lakes, and manu unspoiled beaches and
archipelagoes. The different national races and their way of life, traditional
arts and crafts offer exotic vistas of the nation while the warm hospitality of
Myanmar people world-renowned.

なぜミャンマーなのか?
ミャンマー人は日本との親和性が高い最も好ましい人材と言えます。高い就労意欲を持つことや国民の90%が仏教徒であること、また識字率の高さから教育水準が相対的に高い若年層の人材が多いことから、今後の成長が見込まれる「ラストフロンティア」として注目されています。
国民の90%が敬虔な仏教徒であることや高い就労意欲を持つことなど、ミャンマー人は日本人に近い国民性を持っています。また識字率の高さや日本語の上達スピードの速さなど、高い教育水準を持った優秀な若者が多いのですが、良い仕事に就けるチャンスが少なく、日本で働きたいという意欲を強く持っています。
ジーエーエス カンパニーリミテッド
ミャンマーギャラリー











